If you’re experiencing aches & pains, having trouble with movement or mobility within the body, or even recovering from an injury, there are several types of practitioners available who may be able to help you. But who should you see? It can be so confusing!
Physiotherapy, Chiropractic, Osteopathy: What’s the difference?
All three take a slightly different approach to treatment, so it can be difficult to know which one might be right for you.

Physiotherapists specialise in the diagnosis & management of movement disorders. The aim is to rehabilitate & improve a person’s ability to move & function, often following injury or surgery. A Physiotherapist uses massage, stretching, & will prescribe exercises to achieve these aims.
Chiropractors core focus is the diagnosis & correction of disorders of the musculoskeletal system, commonly the spine, using manual adjustments (manipulation). It can also involve a combination or hands-on care, physical therapy modalities (ultrasounds) & exercise prescription.
Osteopaths focus on the health & well-being of the entire body, rather than just the injured or affected part. They focus on how the skeleton, joints, muscles, nerves, circulation, connective tissue & internal organs function as a holistic (whole body) unit. Osteopathy recognises the important link between the body’s structure & the way it functions.
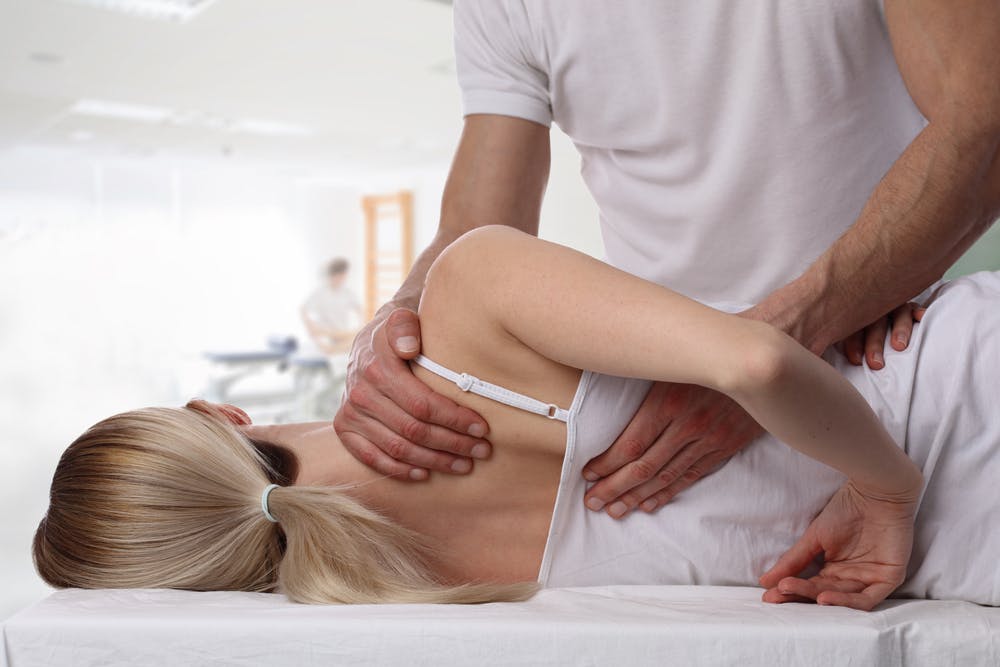
As with Physiotherapists & Chiropractors, Osteopaths use their hands to try & balance the systems within the body. Osteopaths also focus on other hands-on techniques including soft/deep-tissue massage, muscle-stretching, trigger-point release, joint-mobilisation, postural/ergonomic advice, exercise-prevention ‘home-work’, & even nutritional advice.
Patients of Osteopaths commonly include those with back & neck pain, sciatic-type problems, headaches, joint-pain, but they also treat more than what you may think – Osteopaths can also help alleviate the signs & symptoms of work-related & repetitive strain injuries, sports injuries, whiplash, tennis elbow, knee pain, shin-splints, heel/foot pain, & muscular strains & tendinopathy.
Osteopaths generally work in private practice & do not require a referral. Treatment is covered by most private health funds & the Chronic Disease Management (CDM) Medicare scheme. Osteopathy degrees take 5 years to complete & practitioners must be registered by law with the Australian Health Practitioner Registration Agency.
Call us on 9042 1056 to discuss how Osteopathy can help with your health concerns!




